Denis Zeile
Master's Programme in Architecture and Urban Design
Umeå School of Architecture
Specialisms: Architecture / Interior Design /
Location: Riga, Latvia


Denis Zeile

First Name: Denis
Last Name: Zeile
Specialisms: Architecture / Interior Design
Sectors:
My Location: Riga, Latvia
University / College: Umeå School of Architecture
Course / Program Title: Master's Programme in Architecture and Urban Design
About
I am Denis Zeile, a design professional with a rich 6-year journey encompassing both architecture and interior design across the global stage. My career has flourished in iconic cities such as London, Los Angeles, Riga, and Dubai, each contributing to my versatile perspective. With every project, I endeavor to unite imaginative aesthetics with environmentally conscious solutions. It is my belief that design should not only inspire but also harmonize with our planet.
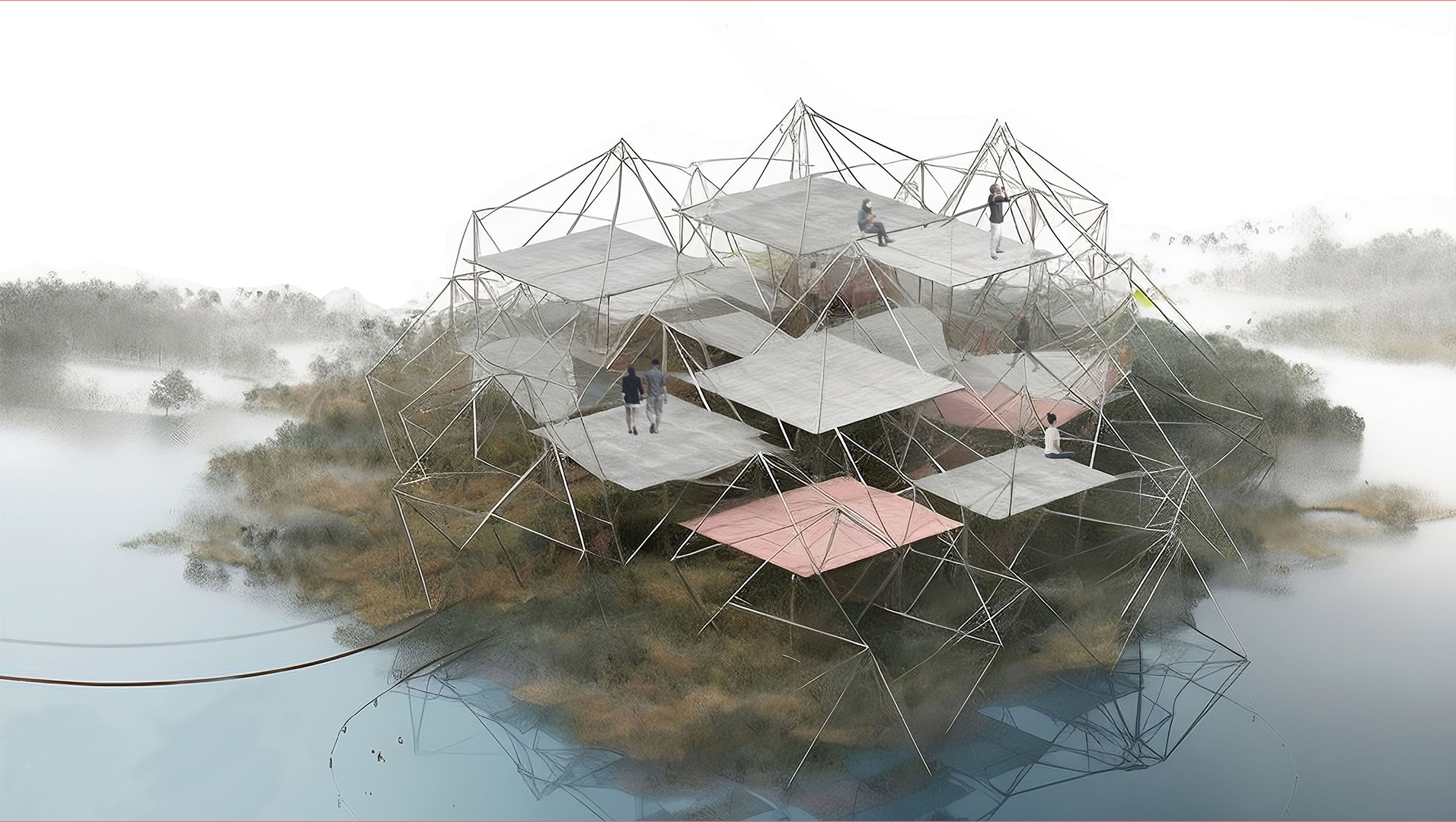
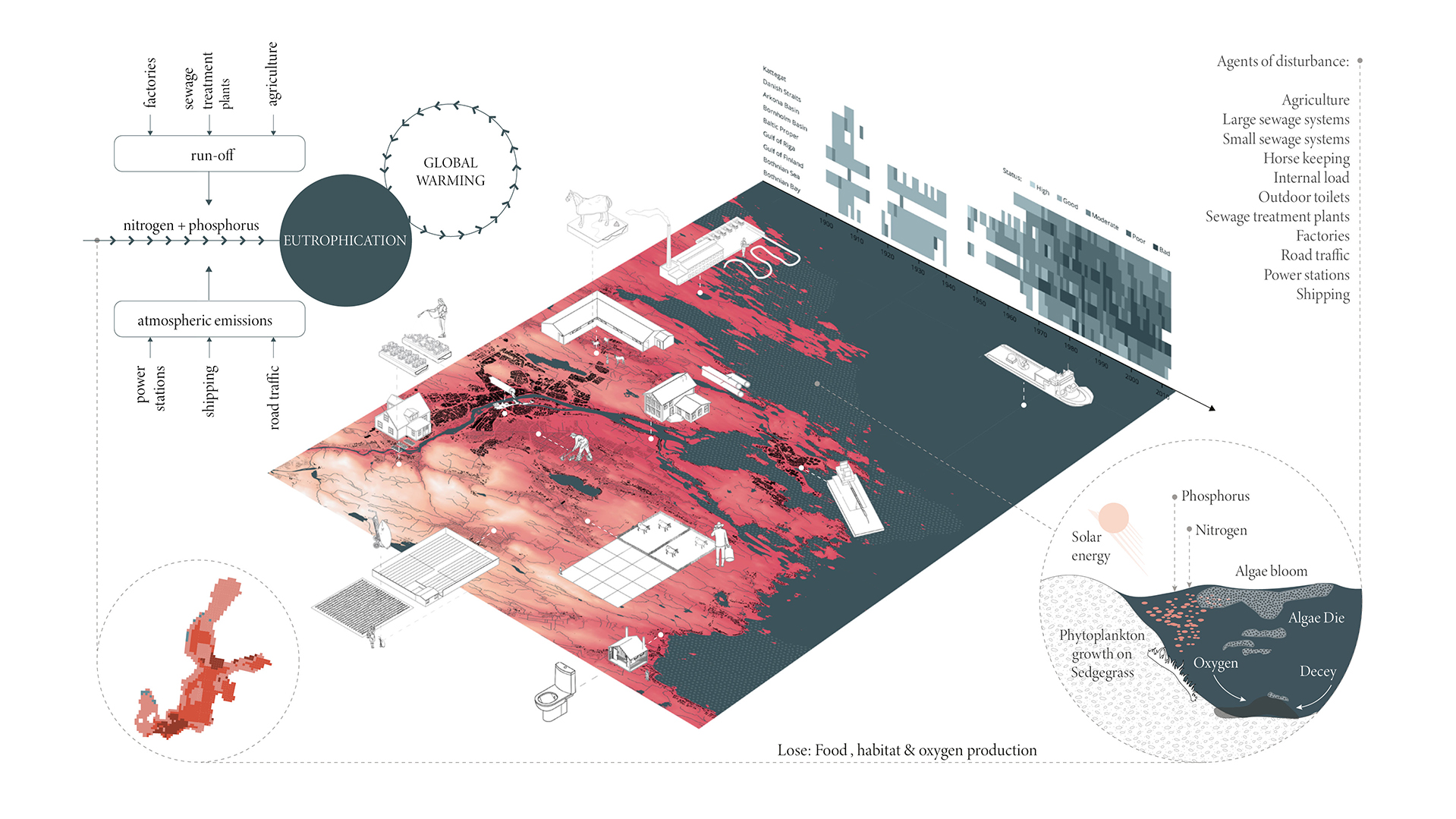
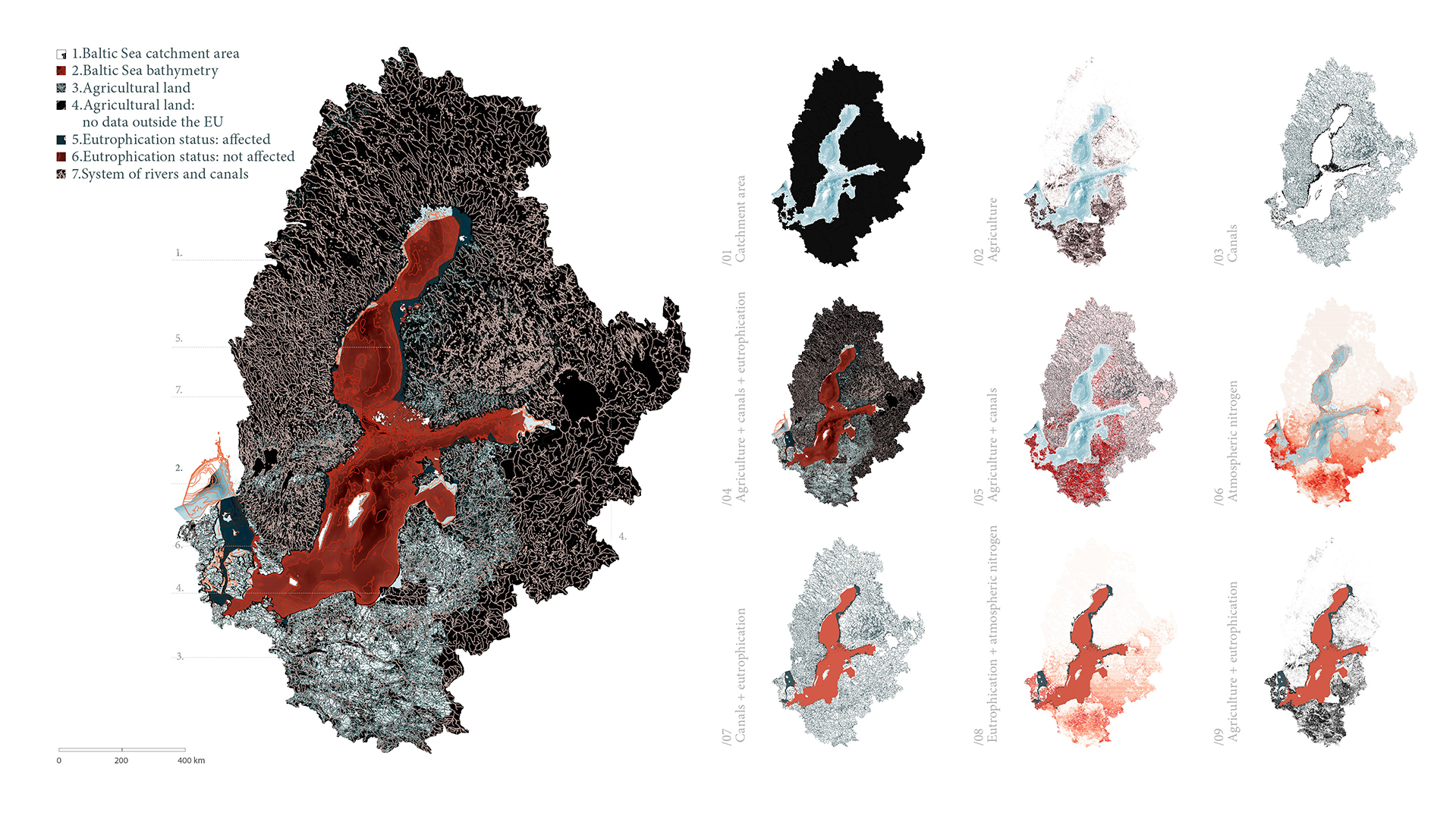
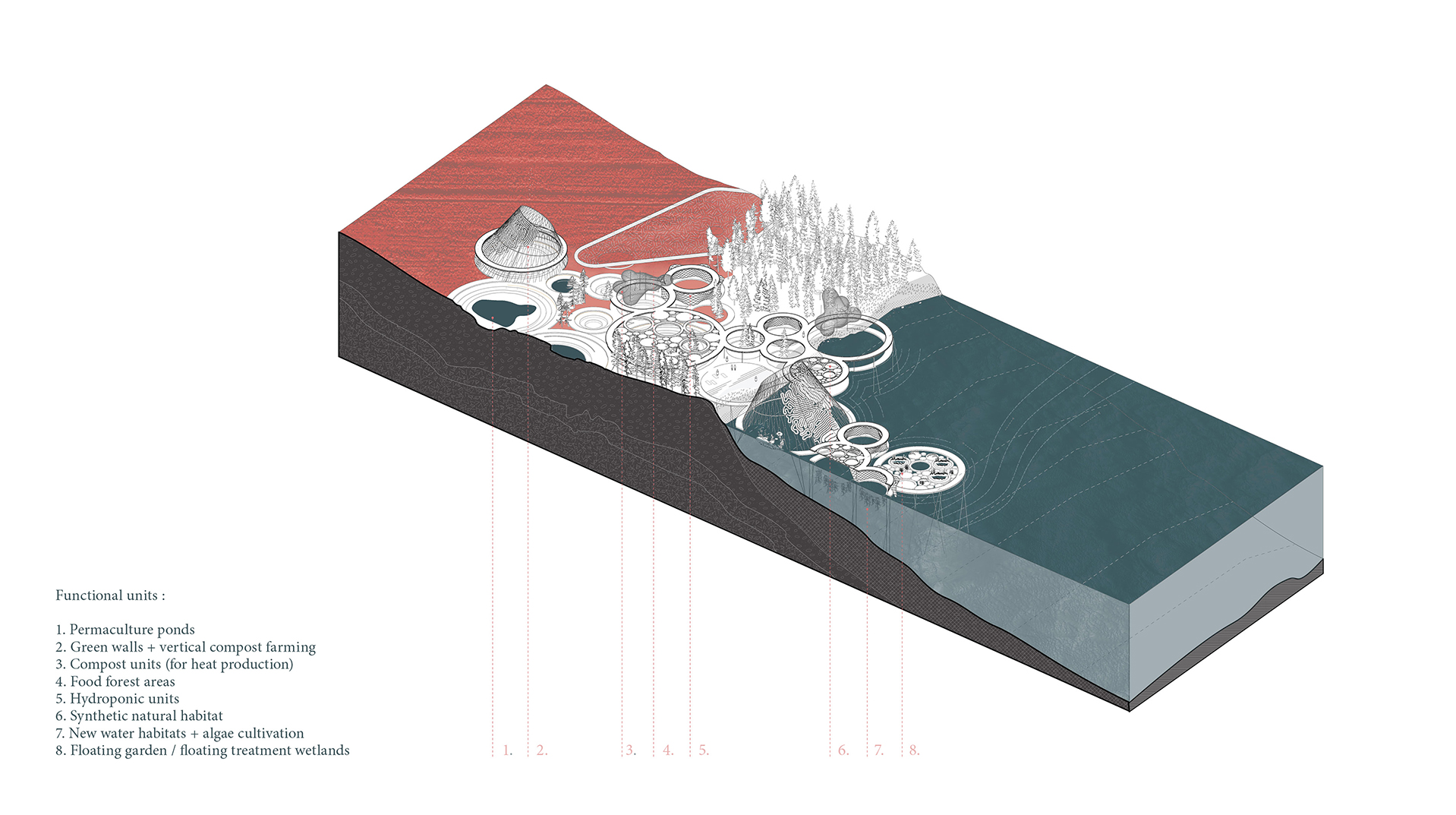
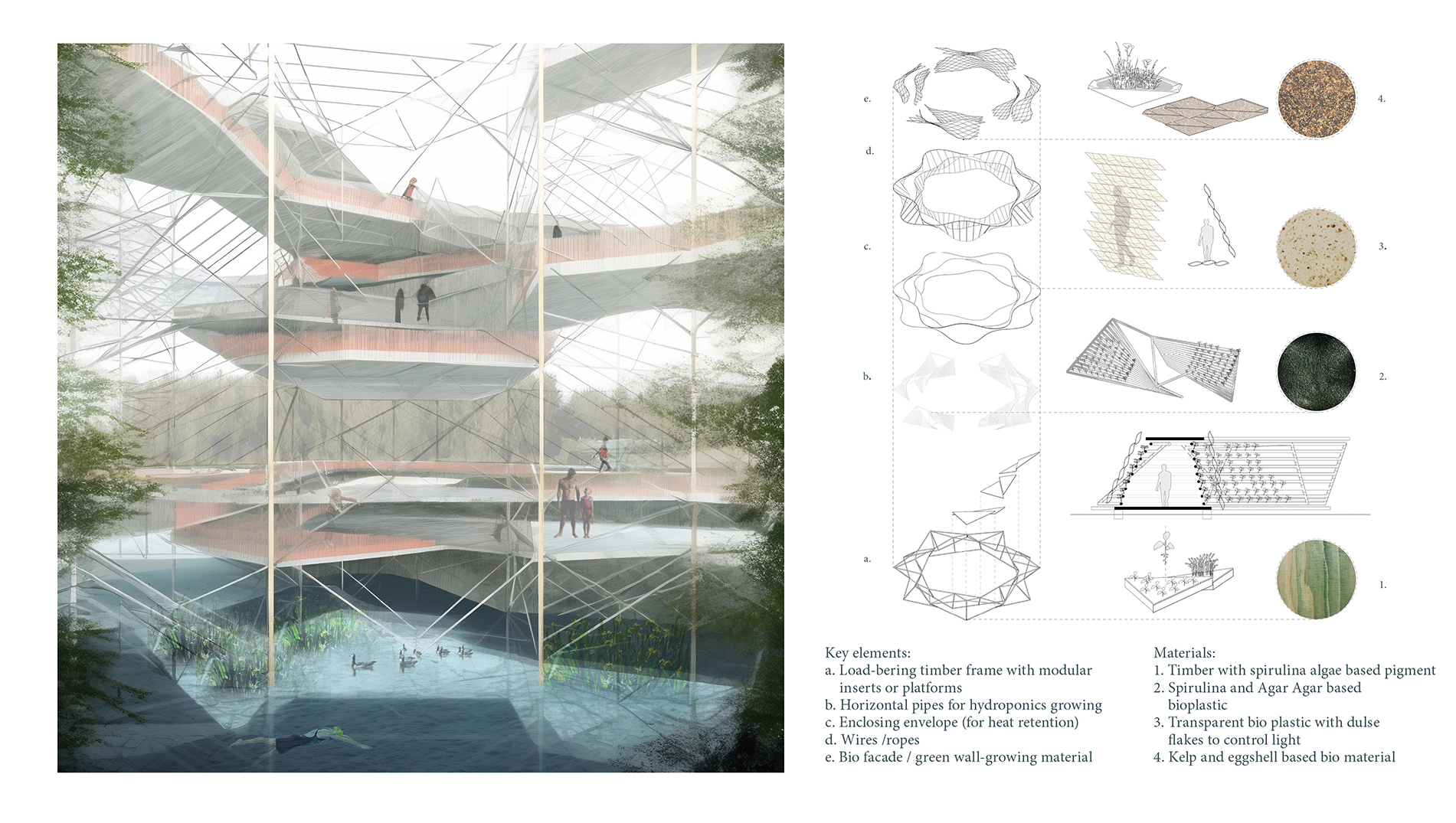
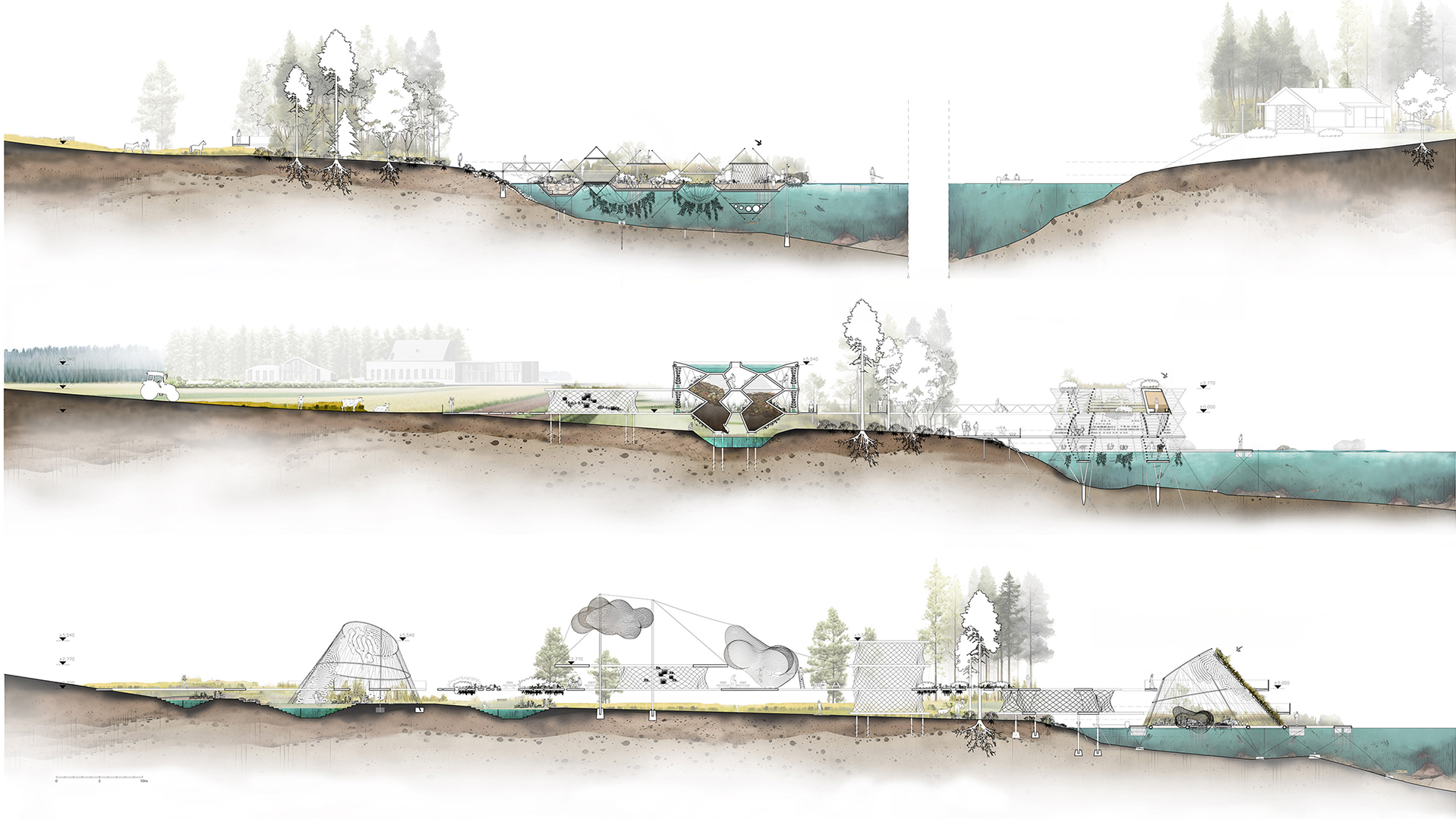
Algal blooms and the reduction of the seabed’s oxygen have a particularly negative impact on the Baltic Sea, caused by the eutrophication process. The process of eutrophication involves the gradual enrichment of a body of water, or portions of it, with minerals and nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorus. In Sweden, agriculture is the source of almost half of the nitrogen and phosphorus released into the environment. (Swedish Board of Agriculture 2013) As a result of eutrophication catalysed by climate change, marine biodiversity and fish stocks suffer also reducing the welfare of citizens. Around 30% of the total nitrogen inputs come from atmospheric sources, mostly combustion operations connected to shipping, road traffic, energy generation, and agriculture. (HELCOM 2017) Despite the fact that nutrient leakage has decreased in recent years, 97% of the surface of the Baltic Sea is still affected by eutrophication (HELCOM 2017). Taking this as an emergency call, research aims to investigate on how architecture can become a catalyst for environmental regeneration, resulting in a net positive outcome. The research refers to the theory of regenerative design, which has received particular attention in recent years in addressing constraints of sustainability. The design proposal aims to spatialize regenerative processes operating on different scales, from bio-material development to an urban masterplan. The research envisions a regenerative approach to the Baltic Sea by introducing a network of interventions operating on the transitional zone between agricultural fields and rivers transmitting nutrient pollution to the sea as part of its catchment basin. The design proposal integrates regenerative strategies learned from case studies and a literature review. Research speculates on how to reduce excessive nutrient enrichment in soil, water and decrease anthropogenic nutrient loading, while engaging with the local community through eco-recreation. Enlisting nature as a guide and referring to biomimicry as the model, the network of various functional zones suggests bioremediation of polluted agricultural fields.
Competitions